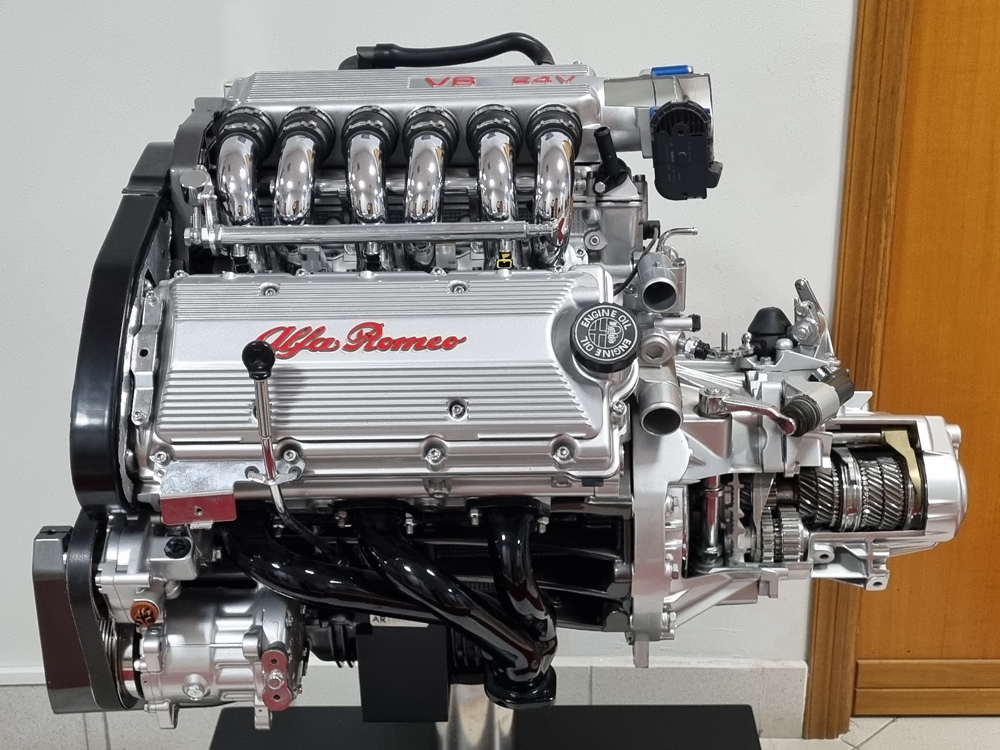






At the end of the 1960s, Alfa Romeo began the development of a new 60° V-6 engine intended for its medium and high-class cars, to replace the previous in-line six-cylinder model. After a slowdown of the project due to the consequences of the 1973 Oil Crisis, in 1979 the first version of the engine made its debut with a displacement of 2.5 litres, equipping the Alfa 6 sedan and then the GTV 6 coupé. In the following years the engine was the subject of various technical and performance developments, which gave rise to various models ranging from two to three litres, including a supercharged 2-litre version. These engines were used for a long time in various models, including the Alfa Romeo 75, 164, 155, 166 and 156, and other Lancia and FIAT sedans, as well as in racing cars by means of appropriate modifications. In 1992 the V6 engines was renewed through the use of new heads with 4 valves per cylinder, initially introduced in the 3-litre engine. From this was derived the 2.5 litre 190 HP version for the Alfa Romeo 156 sedan, presented in 1997, and later also used in some versions of the higher class 166 model. Thanks to its technical and performance qualities, in 2000 the 2.5 litre engine received the prestigious international “Engine of the year award” for displacement class between 2 and 2.5 litres. Together with the 2.5 litre engine, the more powerful 3.2 litre version with 250 HP, presented in 2002 for the sportier GTA versions of the 147 and 156, was the last of the Alfa Romeo V6 engine series commonly called "Busso", from the surname of one of its most famous designers. Both the 2.5 and 3.2 litre models were also the last engines to be produced until 2004 in the historic Arese plant in Milan, which nowadays host to the Alfa Romeo Historical Museum.
Click here to listen to the audioguide on izi.TRAVEL
Alfa Romeo 156 and 166
Courtesy of Museo Storico Alfa Romeo